Autocratic versus Democratic Leaders

 |
Autocratic versus Democratic Leaders |
 |
|
Articles | Books | Dictionary | Faq | Home | Leaders | Organizations | Search
|
Leadership ContinuumTannebaum and Schmidt |
Summary of the Leadership Continuum. Abstract |
R. Tannebaum and W.H. Schmidt 1973 |
The Leadership Continuum model of Tannebaum and Schmidt (1973) suggests that autocratic leaders are more likely to make their own decisions and not engage their subordinates, whereas a more democratic leader (laissez-faire manager) gives subordinates a greater degree of delegation in decision-making.
In 1938, Lewin and Lippitt proposed classifications of leaders based on how much involvement leaders placed into task and relationship needs. This range of leadership behaviors was expressed along a continuum by Tannebaum & Schmidt in 1973, ranging from boss-centered (task) to subordinate-centered (relationship).
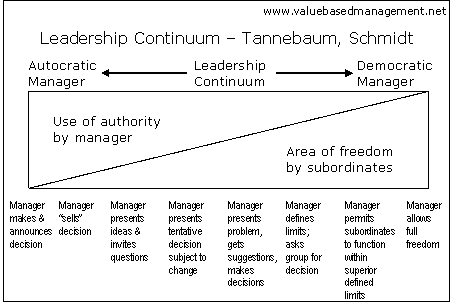
To choose the most appropriate
style and use of authority, the leader must consider:
Forces in the manager: belief in team member participation and confidence in capabilities of members.
Forces in the subordinate: subordinates who are independent, tolerant of ambiguity, competent, identify with organizational goals.
Forces in the situation: team has requisite knowledge, team hold organizational values and traditions, teams work effectively.
Time pressure: need for immediate decision under pressure mitigates against participation.
Advantages of the Model
Gives managers a range of choices for involvement.
Presents criteria for involvement and delegation.
Focuses decision maker on relevant criteria (e.g., forces & time).
Emphasizes employee development and empowerment.
Is heuristic--encourages research to see how effective delegation may be under the model.
Limitations of the Theory
Involves only the initial step of assigning a task to someone, not the following processes that may determine the effectiveness of the outcome.
Assumes the manager has sufficient information to determine disposition to self or team.
Assumes "neutral" environment without social bonds or politics.
Simplifies complex decisions to a two-polar dimension; more simple than reality is.
| 👀 | TIP: To learn more, have a look at the Leadership Continuum center: Summary, forum, tips and tools. |
Compare with the Leadership Continuum: Path-Goal Theory | Leadership Styles | Theory X Theory Y | Contingency Theory | Competing Values Framework | Levels of Culture | Expectancy Theory | Results-Based Leadership | Result Oriented Management | Hierarchy of Needs | Herzberg Two Factor Theory | Bases of Social Power | Seven Surprises | Seven Habits | SMART | PAEI | Changing Organization Cultures | Framing
About us | Advertise | Privacy | Support us | Terms of Service
©2025 Value Based Management.net - All names tm by their owners