Existence, Relatedness, Growth Theory

 |
Existence, Relatedness, Growth Theory |
 |
|
Articles | Books | Dictionary | Faq | Home | Leaders | Organizations | Search
|
ERG Theory |
Summary of Existence, Relatedness, Growth Theory. Abstract |
Clayton P. Alderfer |
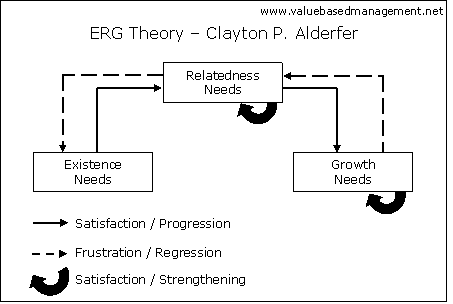
The ERG Theory of Clayton P. Alderfer is a model that appeared in 1969 in a Psychological Review article entitled "An Empirical Test of a New Theory of Human Need". In a reaction to Maslow's famous Hierarchy of Needs, Alderfer distinguishes three categories of human needs that influence worker’s behavior; existence, relatedness and growth.
These ERG categories are:
- Existence Needs: physiological and safety needs (such as hunger, thirst and sex)(Maslow's first two levels)
- Relatedness Needs: social and external esteem (involvement with family, friends, co-workers and employers)(Maslow's third and fourth levels)
- Growth Needs: internal esteem
and self actualization (desires
to be creative, productive and to complete meaningful tasks)(Maslow's fourth and fifth levels)
Contrarily to Maslow's idea that access to the higher levels of his pyramid required satisfaction in the lower level needs, according to Alderfer the three ERG areas are not stepped in any way.
The ERG framework recognizes that the order
of importance of the three Categories may vary for each individual.
Managers must recognize that an employee has multiple needs to satisfy
simultaneously. According to ERG, focusing exclusively on one
need at a time will not effectively motivate.
In addition, the ERG model acknowledges that if a higher level need remains unfulfilled, the person may regress to lower level needs that appear easier to satisfy. This is known as the frustration-regression principle. This frustration-regression principle impacts workplace motivation. For example, if growth opportunities are not provided to employees, they may regress to relatedness needs, and socialize more with co-workers.
If management can recognize these conditions early, steps can be taken to satisfy the frustrated needs until the subordinate is able to pursue growth again.
Book: Clayton P. Alderfer - Existence, Relatedness, and Growth; Human Needs in Organizational Settings
| 👀 | TIP: To learn more, have a look at the ERG Theory center: Summary, forum, tips and tools. |
Compare with ERG Theory: Hierarchy of Needs | Herzberg Two Factor Theory | 4 Dimensions of Relational Work | Emotional Intelligence | Expectancy Theory | Path-Goal Theory | Theory X Theory Y | Hofstede | What is Value Based Management?
About us | Advertise | Privacy | Support us | Terms of Service
©2025 Value Based Management.net - All names tm by their owners