Acid-test Ratio

 |
Acid-test Ratio |
 |
|
Articles | Books | Dictionary | Faq | Home | Leaders | Organizations | Search
|
Measuring liquidity: Acid-test Ratio
The Quick Ratio (QR) method is a model for measuring the liquidity of a company by calculating the ratio between all assets quickly convertible into cash and all current liabilities. It specifically excludes inventory. It is an indicator of the extent to which a company can pay current liabilities without relying on the sale of inventory.
Typically, a QUR of 1:1 or higher is good
and indicates a company does not have to rely on the sale of inventory to
pay the bills.
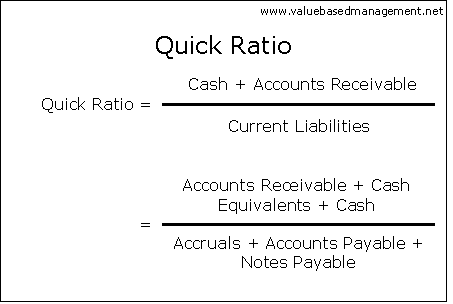
For the Quick Ratio formula, see the picture.
This ratio is also known as the Acid-test Ratio.
A thing to remember when using the QR model is that it ignores timing of both cash received and cash paid out.
Take the example of a company with no bills due today, but lots of bills that are due tomorrow. This company may show a good quick ratio, but can not be considered as having a good liquidity.
Book: Steven M. Bragg - Business Ratios and Formulas : A Comprehensive Guide
Book: Ciaran Walsh - Key Management Ratios
| 👀 | TIP: To learn more, have a look at the Quick Ratio center: Summary, forum, tips and tools. |
Compare also: Current Ratio |
Cash Ratio |
Z-Score |
Discounted Cash Flow |
Free Cash Flow |
Economic Value Added |
CFROI
About us | Advertise | Privacy | Support us | Terms of Service
©2025 Value Based Management.net - All names tm by their owners